Hydroquinone Cream in NZ: A Comprehensive Guide
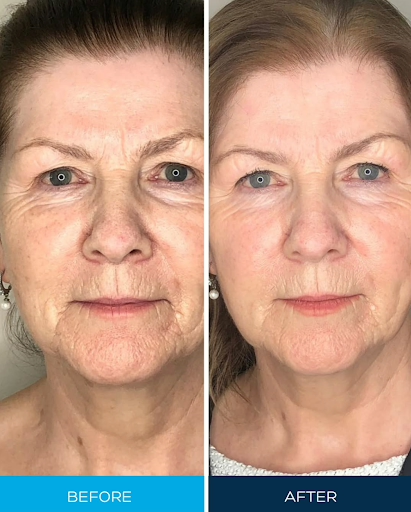
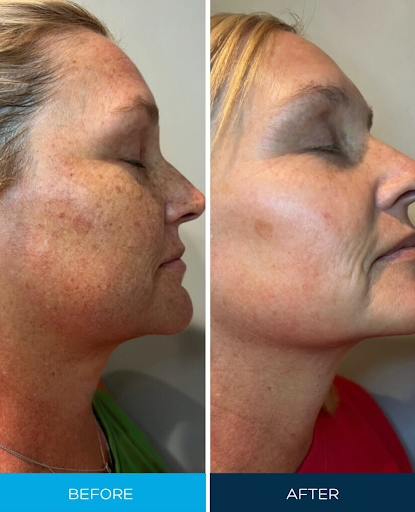
If you want to lighten your skin or fade melasma and uneven pigmentation, you may consider using hydroquinone cream. In New Zealand, you must see a doctor and get a prescription to use any cream with hydroquinone.
Let’s delve into everything you need to know about hydroquinone cream and how to obtain it in New Zealand.
What is hydroquinone cream in NZ?
People often use hydroquinone cream to lighten the skin and treat uneven pigmentation, melasma, and age spots. It works by decreasing the melanin production in the skin, which helps to lighten dark spots and even out skin tone. This makes it a popular skin-bleaching agent.
Why was hydroquinone cream taken off the shelves in New Zealand?
New Zealand took hydroquinone cream off the shelves due to concerns about its potential side effects.
Research suggests that long-term use of hydroquinone may increase the risk of developing skin cancer. In South Africa, some people use a lot of this cream for long periods of time to whiten their skin. This extreme overuse caused a blue discolouration of the skin called ochronosis.
The New Zealand government now requires a doctor’s prescription for hydroquinone to ensure its safety and control of use.
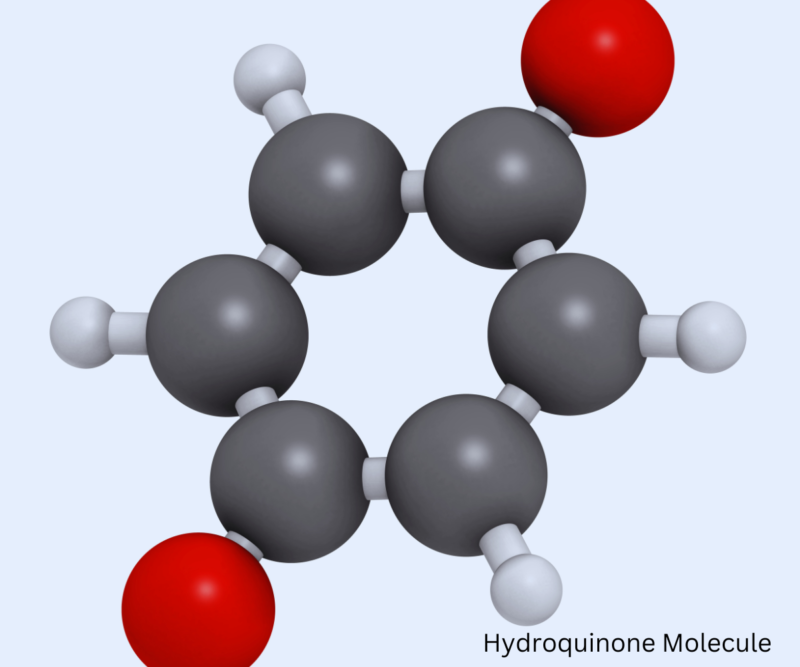
Does hydroquinone bleach or whiten the skin?
A research study in 2016 showed that hydroquinone lightens the skin after eight weeks of use. It can lighten the darker and hyperpigmented areas of the skin, but it also lightens the normal skin. In South Africa, many people used large amounts over quite long periods, sometimes even up to years, to lighten the skin. As a result, doctors in South Africa observed that many of these people developed a blue skin discolouration.
This is unlikely to happen if you use hydroquinone for only short periods of time and in small amounts.
What does it treat?
Doctors often use hydroquinone to treat skin conditions that cause excessive pigmentation and brown discolouration. It works by reducing melanin production in the skin. Melanin is the pigment that gives the skin its colour. Hydroquinone can help lighten dark spots and even skin tone by reducing the amount of melanin produced. Many research studies could prove that hydroquinone works well, reducing many forms of pigmentation. Nevertheless, most research studies recommend hydroquinone to treat melasma.
Let’s look at how often doctors use hydroquinone for which type of pigmentation.
Most commonly used in Hydroquinone in NZ
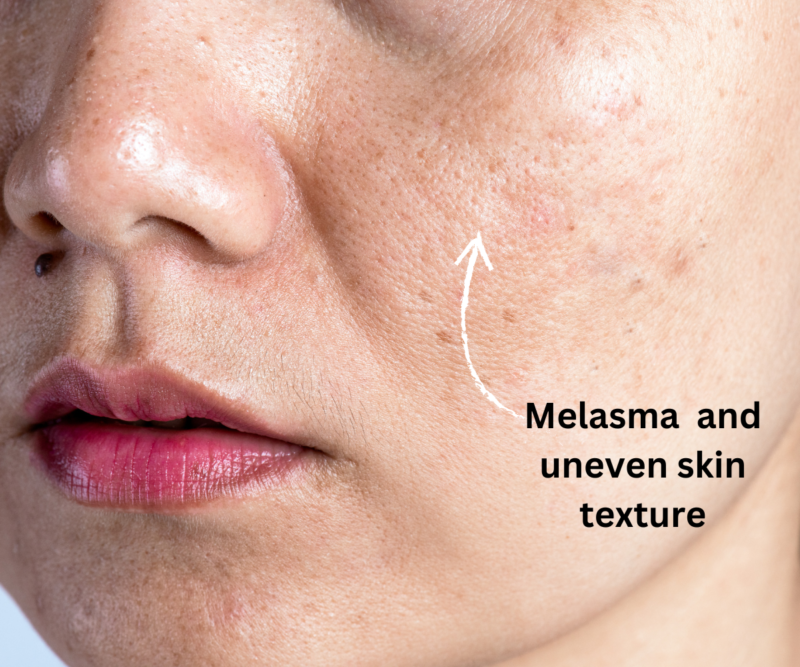
- Melasma
Melasma is a skin condition caused by hormones, sun exposure, and genetics. It causes dark patches on the skin. Many other treatments, like laser or IPL, are less effective than Hydroquinone for treating this condition.
Because of this, hydroquinone, often in combination with Vitamin A and steroids, remains the gold standard for treating melasma.
Not so commonly used
- Uneven pigmentation of the skin
- Age spots and freckles.
- Whitening for darker skin types
- Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Hydroquinone is not as commonly used to treat uneven skin pigmentation, age spots, and freckles. These conditions may require different treatment options, such as laser, chemical peels, or IPL.
Rarely used in NZ
- Skin whitening
In New Zealand, people rarely use hydroquinone to whiten the skin. This is because whitening and maintaining a whiter skin tone would require large amounts over the long term. This could lead to a higher risk of skin cancer and blue discolouration of the skin.
Some clinics in New Zealand provide safe glutathione infusions with a doctor’s supervision to help lighten skin colour.
Why do you need to prescribe it?
A doctor must prescribe it to ensure it is a safe formulation. In the past, some skin care products with hydroquinone were questionable or even dubious. This was particularly true in countries with less strict regulations than New Zealand.
Hydroquinone can cause skin irritation, redness, and darkening without medical supervision. If used too long or too much, it can cause skin cancer or blue discolouration.
Doctors can prescribe hydroquinone, monitor its usage, and ensure patients use it safely and effectively. To avoid bad reactions, follow the doctor’s instructions carefully and don’t use too much. You need a prescription for hydroquinone to protect your health and well-being.
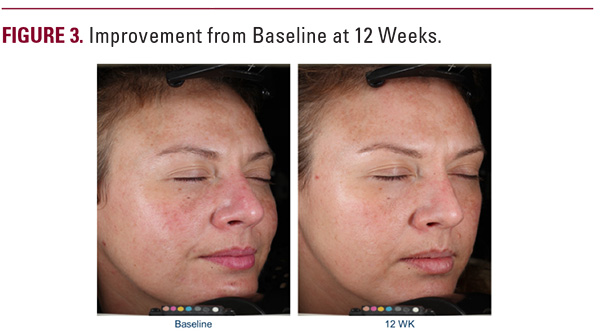
What are the most popular alternatives to hydroquinone cream in NZ?
There are many alternatives to hydroquinone cream. However, not many research studies have examined their effectiveness in comparison to each other. But we do know that each of the following ingredients fades pigmentation. The most popular ingredients are:
Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP)
This is a form of Vitamin C that helps reduce hyperpigmentation and brighten the skin. People know MAP for its antioxidant properties, which protect the skin from environmental damage and promote collagen production. One study showed that approximately 50% of people who apply this form of Vitamin C to their skin notice less pigment.
Glutathione
Glutathione is an antioxidant produced in cells. Glutathione has become very popular as a skin-whitening treatment. However, it does not treat melasma or uneven pigmentation very well. So, if this is your main concern, you may be better off with hydroquinone cream.
Glutathione is available as a supplement or cream. Some people get infusions to whiten their skin.
Cysteamine
Cysteamine cream is a skin-lightening cream that works well for melasma and other types of uneven pigmentation. It appears safe and well-tolerated, but one research study showed it was slightly less effective than hydroquinone cream. It would certainly be a good alternative to hydroquinone as it appears gentler on the skin.
This cream is available at some chemists and warehouses, and some doctors may offer it in their clinics.
Arbutin
Arbutin is another popular alternative to hydroquinone cream.
Arbutin is actually a compound of hydroquinone and D-glucose. Cosmetics often use arbutin and other ingredients, such as Vitamin C, to lighten skin. Researchers studied how well arbutin works alone or with other ingredients. They found that combined therapy with arbutin and laser could enhance depigmenting efficacy.
Arbutin is a safer and gentler alternative to hydroquinone, but its effectiveness compared to hydroquinone is still unknown.
Other ingredients
Research shows that many other products currently lighten skin or are under study. Some of these, such as kojic acid, glycolic and azelaic acids, are well-known to most skin doctors.
A summary about Hydroquinone NZ
Doctors must prescribe and oversee hydroquinone treatment to ensure its safety. A small amount of hydroquinone cream used briefly likely won’t cause skin cancer or blue skin discolouration.
Researchers are investigating many other ingredients, with cysteamine being the most promising. But at this stage, hydroquinone cream remains the gold standard for treating melasma. For other forms of pigmentation, such as dark spots, it is preferable to try laser or IPL treatments.
Your appointment at Satini Cosmetic Clinic
will allow our experienced doctors to assess your skin condition and recommend the most suitable treatment. If you have melasma, dark spots, or other pigmentation issues, our team will help you get the best results.
We know how important it is to feel good about your skin. Our goal is to offer safe and effective solutions for all our patients. Contact us today to schedule your free initial consultation and take the first step towards achieving clear, radiant skin.